Chinese AI startup DeepSeek has shaken up the market with its groundbreaking AI model, R1. The company claims it trained the model for just $5.6 million—a fraction of what OpenAI spent on its latest generative AI system. R1 still managed to outperform major U.S. tech companies despite lacking access to advanced semiconductors from chipmaker Nvidia.
What’s even more surprising is that R1 is open-source and free to use, something rarely seen among top AI companies. Thanks to its cutting-edge capabilities and user-friendly costs, users around the world have quickly embraced the model. The arrival of R1 marks a significant milestone, proving that companies can develop powerful yet cost-effective AI models.
However, concerns also arise regarding DeepSeek data privacy, with some questioning whether DeepSeek is excessively collecting and utilizing personal information.
Controversies Surrounding DeepSeek
Experts and users who have tested DeepSeek have raised concerns about data security, transparency, and potential biases. These issues have sparked debates over privacy risks, ethical AI practices, and the broader implications of its use.
Data Privacy Concerns
One major issue is the suspicion that DeepSeek collects excessive amounts of user data. According to its Privacy Policy, the platform gathers information such as usernames, birthdates, IP addresses, and device identifiers. What’s particularly alarming is that this data is reportedly transmitted in real-time to servers in China. As a result, countries like South Korea and Italy have taken measures to ban the installation and use of the DeepSeek app, citing concerns over DeepSeek data privacy and national security.
Unauthorized Use of Data
Another pressing concern is the unauthorized use of data. High-performing AI models require vast amounts of training data, but DeepSeek has not disclosed exactly which datasets it used to develop R1. Some speculate that the company may have scraped data from the web, raising potential copyright infringement issues. If an AI model is trained on unlawfully obtained data, it could face legal disputes, ultimately discouraging businesses from adopting it.
Furthermore, OpenAI has claimed that it has repeatedly observed attempts by China-based organizations, including DeepSeek, to extract large volumes of data from its AI tools. In particular, concerns have been raised that DeepSeek may have used a technique called “distillation” to mass-collect OpenAI’s model outputs for training its own AI. Originally, distillation is a method used to optimize and compress AI models. However, if a company leverages another AI model’s outputs as training data, it raises copyright infringement and ethical concerns. If DeepSeek indeed harvested large amounts of OpenAI’s API-generated outputs, this could escalate beyond simple data misuse into a broader issue of transparency and trust in AI model training.
Chinese Bias
The third issue concerns the controversy surrounding the Chinese bias in DeepSeek’s model. Despite being an open-source model, DeepSeek has also faced criticism for potential bias favoring the Chinese government. Some experts suggest that the model’s responses to certain topics align with China’s censorship policies. Given that there is heavy government regulation on China’s internet environment, there is a strong possibility that DeepSeek’s AI model may provide restricted information on specific political and social issues or frame responses in a way that is advantageous to the Chinese government. This is not a technical concern but rather a broader trust issue for global users, as it highlights the risk of AI models reflecting the political and ideological stance of a specific nation.
Key Lessons from the DeepSeek Controversy
The controversy surrounding DeepSeek ultimately suggests that, no matter how advanced an AI model’s performance is, it will struggle to achieve long-term growth and trust if its data sources are unclear or if legal issues exist. Companies are now shifting away from merely adopting powerful AI models; the critical task is ensuring the transparency and legitimacy of the data used to train these models. This tendency suggests that securing trust in the legality and origin of data is becoming a core challenge. As a result, we can expect data management to become increasingly important, with the value of verified data rising sharply.
In this context, the recent attention on the American company Palantir is noteworthy. Palantir provides data analysis and AI-driven decision support systems, positioning data security, refinement, and trust as its core values. Notably, organizations handling sensitive data in sectors like government, military, finance, and healthcare rely on Palantir’s platform to build trusted data environments. This not only highlights the importance of an AI model’s performance but also underscores the significance of data sources and trustworthiness. While AI models like DeepSeek, with unclear data origins and data privacy issues, face controversy, companies like Palantir are gaining more recognition due to their focus on data security and transparency.
The Role of Reliable Data and Flitto in the Evolving AI Market
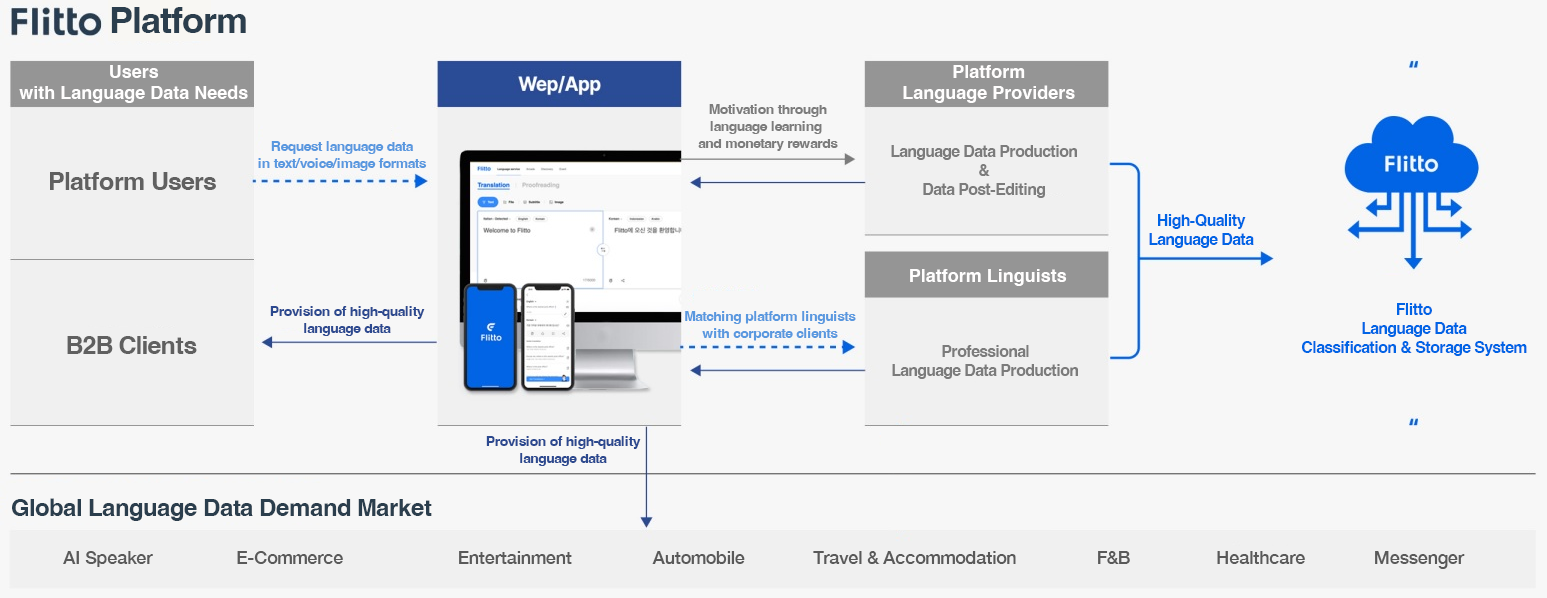
AI model development depends heavily on authentic and reliable data, and we can never overstate its importance. Flitto actively builds reliable datasets and provides verified AI training data. By leveraging its integrated language platform, which serves 14 million users worldwide, Flitto collects and refines data through legally compliant processes, ensuring the development of high-quality AI training datasets. As a result, many global AI companies are already utilizing Flitto’s data to advance their AI models.
As more global companies seek trustworthy data sources, platforms like Flitto become increasingly important, and the legitimacy and reliability of data will solidify as key competitive advantages. In response to these trends in the AI industry, Flitto continues to adapt swiftly, supplying verified data to the global AI market and leading the way in supporting various AI services, including AI translation and interpretation solutions.
